
What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGMS)?
A continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) continuously measures the level of glucose in interstitial fluid, and displays trends and patterns in glucose level changes.
It measures the user’s glucose in real time, and sends an alert before glucose levels fall too low or rise too high. This allows the user to manage their diabetes easily and effectively.
It measures the user’s glucose in real time, and sends an alert before glucose levels fall too low or rise too high. This allows the user to manage their diabetes easily and effectively.
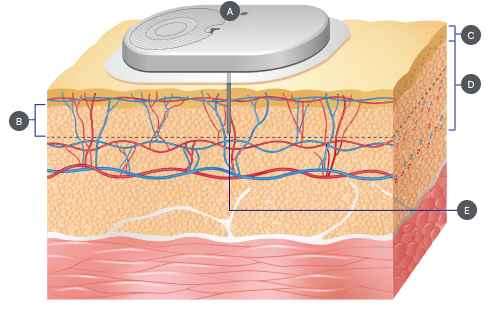
- A. Integrated Transmitter & Sensor
- B. 4~6mm
- C. Skin(1~2mm)
- D. Subcutaneous layer(ca.15mm)
- E. Sensing part
- * Interstitial fluid: body fluid that fills the space around your cells and tissues
How does a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System work?
1When you wear the CGMS, the glucose sensor reaches beneath your skin to the interstitial fluid.
2The surface of the sensor contains enzymes that react with glucose. The reaction generates electrical signals, which the CGMS uses to measure the concentration of glucose in the interstitial fluid.
3The transmitter sends these measurements to your smart device, where they are displayed as graphs and figures in an app.
4Typically it takes five to ten minutes for glucose to move from the blood to the interstitial fluid. As a result, measurements taken using this method don't always match conventional blood glucose monitor readings.
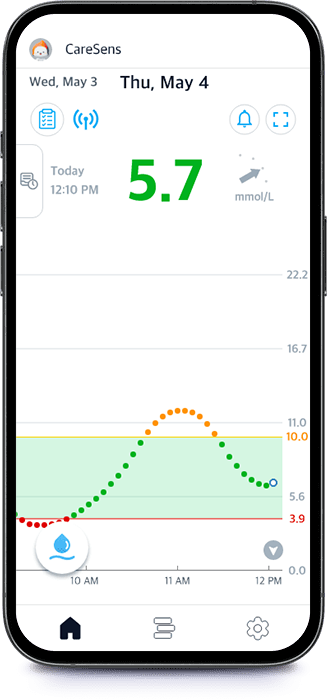

How can I see
my CGMS glucose readings?
my CGMS glucose readings?
Check your glucose changes through
the CareSens Air app on your smart device.
the CareSens Air app on your smart device.
Your CGMS comes with a mobile app that displays glucose measurements and other data. Install the app on your smart device and connect it to your CGMS.
The CGMS will automatically send glucose readings to the app at regular intervals via the transmitting part.
The app displays these readings as visual graphs and numbers, so you can see your glucose levels and track changes in real time.
You can also use the app to track daily routines such as meals, exercise, and medication to help you better manage your diabetes.
The CGMS will automatically send glucose readings to the app at regular intervals via the transmitting part.
The app displays these readings as visual graphs and numbers, so you can see your glucose levels and track changes in real time.
You can also use the app to track daily routines such as meals, exercise, and medication to help you better manage your diabetes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
is Beneficial for
is Beneficial for
Source: Korean Diabetes Association
-

Large fluctuations in blood glucose
-

Severe or frequent hypoglycemia
-
Active insulin therapy or insulin pump use
-

Unexplained elevation in glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c)
-

Changes in insulin therapy

