Detailed Comparison of
CGM and BGM
CGM and BGM
Conventional glucose meters, such as BGM, require the user to measure blood glucose levels at specific intervals. The CGM measures glucose in the interstitial fluid in real time, enabling the user to see trends and patterns in their glucose levels. Conventional glucose meters also require users to intentionally measure blood glucose as needed, whereas, the CGM sensor automatically sends real-time glucose readings to the app without input from the user.
| CGM | vs | BGM |
|---|---|---|
 |
Appearance |  |
| Interstitial Fluid | Sample Type | Fresh Capillary / Venous Whole Blood |

The CGM measures glucose levels automatically using a sensor attached to the back of the upper arm. |
Glucose measurement | 
The user measures blood glucose by drawing blood from the tip of a finger and applying it to a test strip. |
| Once the sensor is attached, the CGMS continuously measures glucose levels for up to 15 days. | Number of measurements | 2-10 times per day(depends on individual differences) |
|
Features |
|
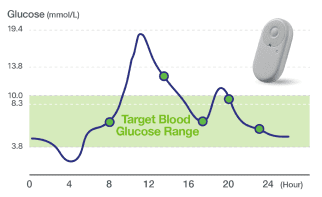
CGM shows continuous glucose readings and glucose trends. |
Difference in Glucose Readings Graph |
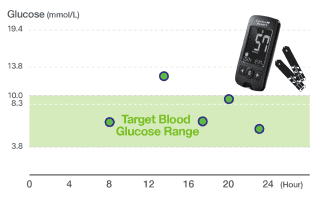
BGM only displays the blood glucose level at the time of testing. |
Why
is the CGM
reading
different from
the BGM
reading?
is the CGM
reading
different from
the BGM
reading?

BGM measures blood glucose directly from the blood, whereas CGM estimates blood glucose concentrations by measuring glucose in the interstitial fluid. Because it takes 5-15 minutes for glucose to move from the blood into the interstitial fluid, this time difference can cause differences in the measurements given by the two methods.
When blood glucose levels are stable, the difference between the two readings (BGM vs CGM) is small; when blood glucose levels fluctuate rapidly, the difference may be greater. Since the trend in blood glucose values is the same in both measurement methods, a system such as CGM that can continuously measure glucose levels, analyze patterns, and notify users of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia can provide users with important advantages in managing their diabetes.
When blood glucose levels are stable, the difference between the two readings (BGM vs CGM) is small; when blood glucose levels fluctuate rapidly, the difference may be greater. Since the trend in blood glucose values is the same in both measurement methods, a system such as CGM that can continuously measure glucose levels, analyze patterns, and notify users of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia can provide users with important advantages in managing their diabetes.

